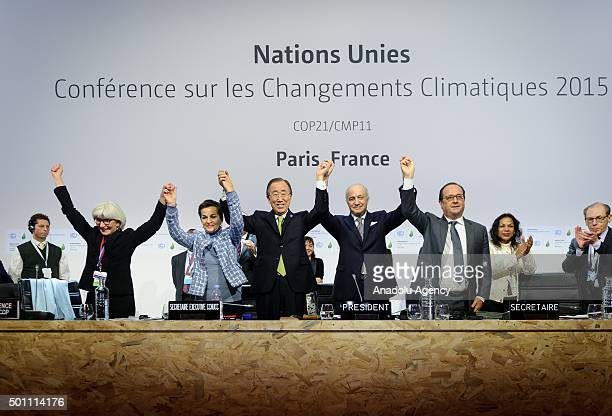
With an increase in global efforts to fight climate change, many notable agreements and protocols were negotiated under the framework of UNFCCC, with some of the most famous known as the Kyoto Protocol in 1997, the Copenhagen Accord in 2009, and the Paris Agreement in 2015.
These agreements have sought to bring together countries from all regions of the world to work together to address climate change and its consequences.
Climate change is one of the most significant threats facing the planet today. The effects of climate change are far-reaching and can cause devastating consequences, including rising sea levels, increased temperatures, and extreme weather conditions.
In 2015, world leaders recognized the importance of taking action to combat climate change and came together to sign the Paris Agreement.
What is Paris Agreement?
Paris Agreement is a legally binding international treaty that aims to limit global warming to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and pursue efforts to limit it to 1.5°C. The agreement requires countries to set and regularly report on their greenhouse gas emissions reduction targets, with the ultimate goal of achieving a climate-neutral world by the second half of the century.
How many countries signed the Paris Agreement?
As of February 2023, the Paris Agreement has 194 member countries, which includes 193 States and the European Union. The agreement entered into force on November 4, 2016, and it includes commitments from all countries to combat climate change.
This number includes China and the United States, the two countries with the largest CO2 emissions among UNFCCC members, and together, these countries represent over 98% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
Understanding the Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement is a crucial step in mitigating the impact of global warming. But what exactly does the agreement entail, and how does it work? Let's take a closer look.
Key Components of the Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement has several key components, including:
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs)
- Long-Term Goals
- Transparency Framework
- Adaptation and Loss & Damage
- Financial Support
Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs)
Each country that has signed the Paris Agreement is required to set and regularly report on its greenhouse gas emissions reduction targets. These targets are known as Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and are updated every five years.
Long-Term Goals
The Paris Agreement aims to limit global warming to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and is making efforts to limit it to 1.5°C. To achieve this, the agreement sets a long-term goal of achieving a climate-neutral world by the second half of the century.
This means that the world's greenhouse gas emissions must be balanced by removing an equivalent amount from the atmosphere.
Transparency Framework
The Paris Agreement has a strong transparency framework that requires countries to report on their emissions reduction progress and provide clarity on their NDCs.
The transparency framework also aims to increase trust between countries and support international cooperation in achieving the agreement's goals.
Financial Support
The Paris Agreement provides financial support to developing countries to help them to shift towards a low-carbon economy and adapt to the impacts of climate change. Developed countries are required to provide financial resources to support the efforts of developing countries.
Impact of the Paris Agreement
Since its adoption in 2015, the Paris Agreement has made significant
progress in addressing the issue of climate change. Some of the key successes
of the agreement include:
- The agreement has brought together countries from all regions of the world to work together to address climate change and its consequences.
- The agreement has led to increased investment in renewable energy and energy efficiency, as well as a shift away from fossil fuels.
- The agreement has helped to raise awareness about the impacts of climate change and the need for action to address it.
- The agreement has increased cooperation among countries to address the issue of climate change, including through the sharing of information, technology, and best practices.
- The agreement has resulted in the development of new policies and measures at the national and international levels to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance resilience to the impacts of climate change.
Why the Paris Agreement failed?
Paris Agreement exactly is not a failure but experts say that it is not enough to prevent the global average temperature from rising up to 1.5°C.
Some of the key failures of the agreement
include:
Lack of Ambition: With all the efforts of the Paris Agreement, many countries have not taken sufficient
action to reduce their emissions and enhance their resilience to the impacts of
climate change.
However, it's important to note that each country's situation is unique, and some may face greater challenges in reducing emissions than others.
Some countries that have been criticized for not taking sufficient action to reduce their carbon emissions include:
- Australia: Even after signing the Paris Agreement, Australia has faced criticism for its lack of action on climate change, particularly in the area of reducing emissions from its large coal industry. In fact, Australia has been ranked as one of the world's worst-performing countries in terms of climate action.
- Brazil: Brazil has also been criticized for not doing enough to reduce deforestation in the Amazon rainforest, which is a significant contributor to the country's carbon emissions. While Brazil has made some commitments to reduce deforestation, progress has been slow, and the country's emissions have continued to rise.
- Saudi Arabia: Being a major oil-producing country, Saudi Arabia has made very limited progress in reducing its carbon emissions. The country has been accused of stalling progress on climate action in international negotiations. Although after attending Saudia Arabia has pledged to go net-zero by 2060 in the COP27 held at Sharm Al-Sheikh Egypt in November 2022, the country is far from reaching this goal as its biggest oil company Aramco has not cut down any of its oil imports.
- United States: Although the United States was a signatory to the Paris Agreement, the previous administration under President Donald Trump withdrew from the agreement in 2019, citing economic concerns. However, the current administration under President Joe Biden has rejoined the agreement and is taking steps to reduce the country's carbon emissions.
Unequal Distribution of Impacts: Climate change is having a disproportionate impact on developing countries,
which are often the least equipped to deal with its consequences. This unequal
distribution of impacts has limited the effectiveness of the Paris Agreement in
addressing the issue of climate change.
According to various studies, the following countries are among those facing the worst effects of climate change:
- Philippines: The Philippines has been fighting the effects of climate change for decades, making it one of the most affected countries. It ranks as the second most affected country in the Global Climate Risk Index 2020, presented by the Germanwatch Institute.
- Bangladesh: The country is highly vulnerable to climate change, as it is a low-lying delta nation, making it susceptible to rising sea levels. It ranks seventh on Germanwatch's Climate Risk Index for cumulative risk between 2000 and 2019.
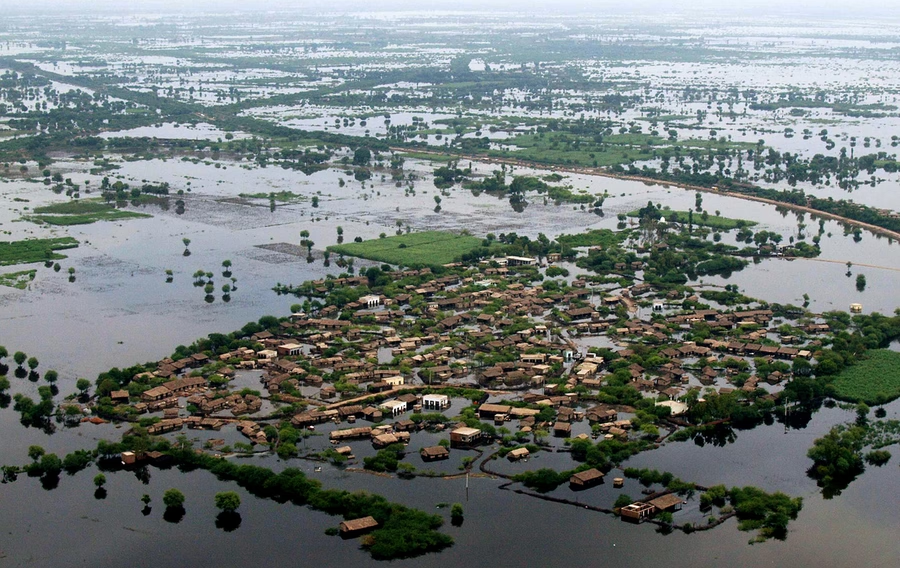
- Pakistan: Pakistan has recently experienced severe floods that caused devastation and loss of life. The country received nearly 190% more rainfall than its 30-year average from June to August of 2022, which resulted in a total of 390.7mm of rainfall. The regions of Sindh and Balochistan in the south were the most affected, with the rainfall in August being 726% and 590% higher than the monthly average.
Although Pakistan is among the countries least responsible for climate change, generating less than 1% of the world's carbon emissions, it is bearing the brunt of its dangerous effects
While the Paris Agreement has set ambitious goals, much more needs to be done to limit global warming to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels.
It is important that countries continue to work together to implement the agreement's provisions and take additional actions to reduce emissions and support the transition to a low-carbon economy.