The CBD is a multilateral environmental agreement that aims to conserve biodiversity, promote sustainable use of its components, and ensure the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from the utilization of genetic resources.
How CBD came into being?
The CBD was born out of growing concerns over the loss of biodiversity due to human activities such as deforestation, habitat destruction, pollution, and excessive use of natural resources.
The idea of a global agreement on biodiversity conservation first emerged in the 1980s, and it gained momentum during the 1990s as the world became more aware of the environmental challenges facing our planet.
The Rio Earth Summit in 1992 was a turning point for the CBD, as it was signed by 150 countries, making it one of the most widely ratified international agreement in history.
What are the main Objectives of CBD?
- The CBD has three main objectives:
- Conservation of biodiversity,
- Sustainable use of its components, and fair, and
Equitable sharing of benefits arising from the utilization of genetic resources.
These objectives are focused on the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity for the benefit of present and future generations.
The CBD recognizes the intrinsic value of biodiversity and the vital role it plays in maintaining ecosystem services such as pollination, water regulation, and carbon sequestration.
How many countries have signed CBD?
As of 2021, the CBD has 196 parties, which include 195 countries and the European Union.
The CBD is open to all countries that wish to join and has a mechanism for non-party stakeholders, including civil society organizations, to participate in its meetings and decision-making processes.
The CBD and meets every two years to review progress in implementing the convention, set priorities for action, and negotiate and adopt new decisions and resolutions.
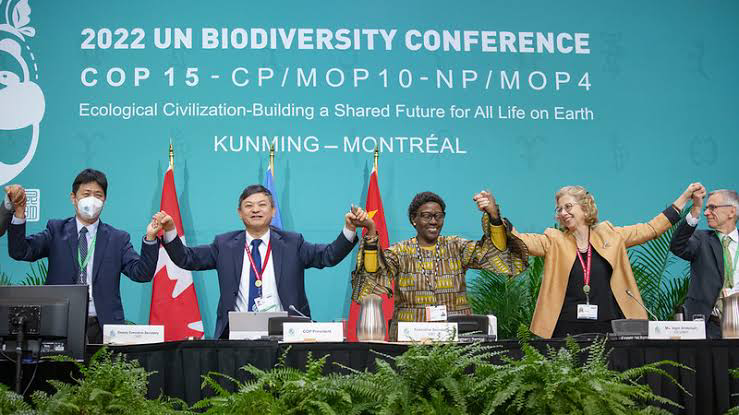
The latest COP15 held in two phases due to COVID-19. Phase one took place virtually, from 11 to 15 October 2021 and included a High-Level Segment from 12 to 13 October. Phase two held in Montreal, Canada, from 7 to 19 December 2022.
Environmental Ministers from 188 countries gathered in Montreal where embarked a very crucial agreement to protect 30% of nature on Earth by 2030.
Main Goals of CBD:
The CBD has set targets for biodiversity conservation and sustainable use, collectively known as the Aichi Biodiversity Targets.
These targets were adopted in 2010 and have half the rate of loss of natural habitat and reduce the degradation of ecosystems, ensuring the conservation of at least 17% of terrestrial and inland water areas and 10% of marine and coastal areas.
Also, restore at least 15% of degraded ecosystems and prevented the extinction of known threatened species and improve their conservation status.
The CBD offers several benefits to its parties and the global community. Firstly, it provides a framework for international cooperation on biodiversity conservation and sustainable use, which is essential given that biodiversity loss is a global problem that requires a collective effort.
Secondly, the CBD promotes the conservation of ecosystems and the services they provide, which are essential for human well-being.
Finally, the CBD recognizes the important role of indigenous and local communities in biodiversity conservation and sustainable use and promotes their participation in decision-making processes.